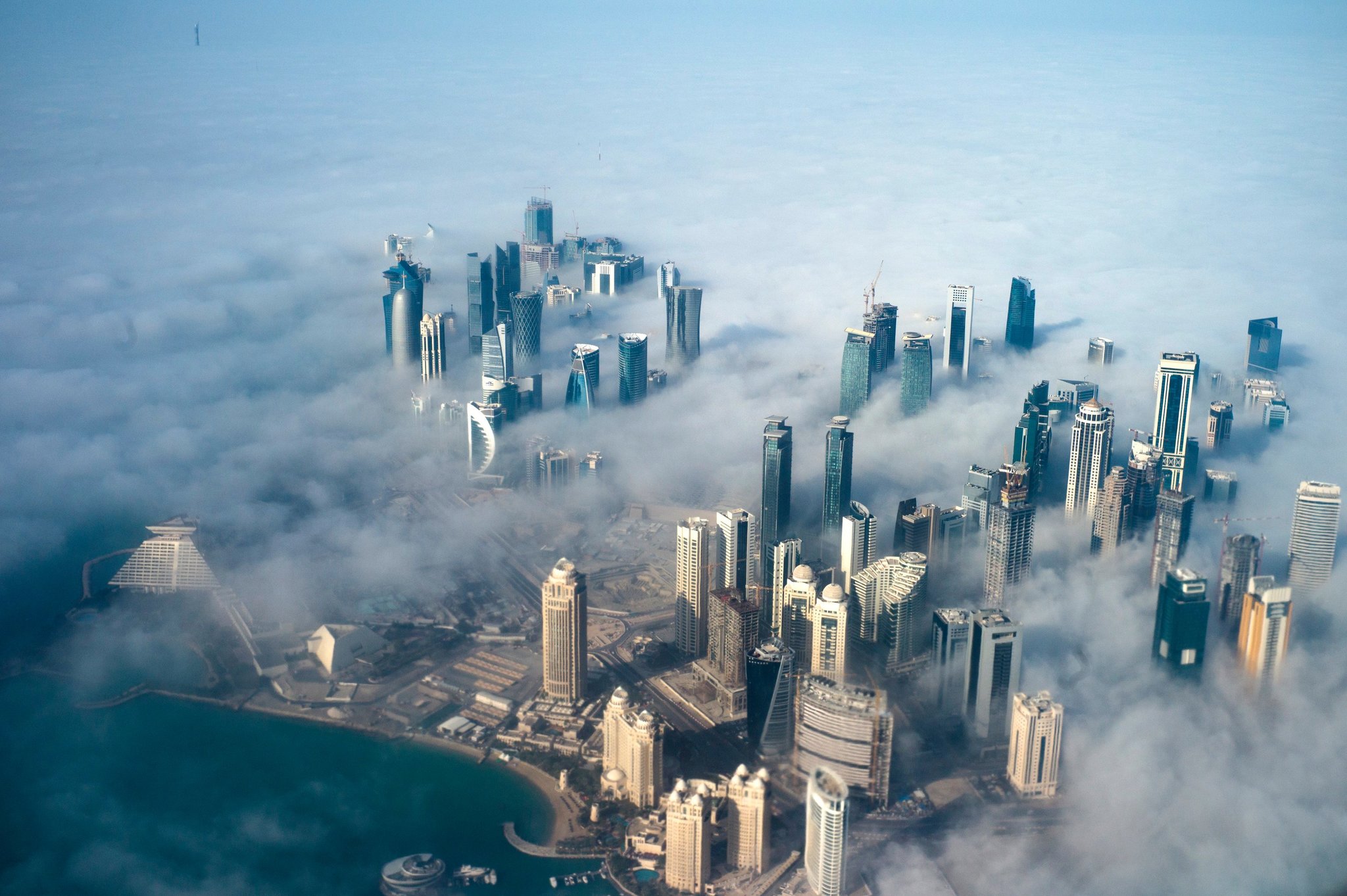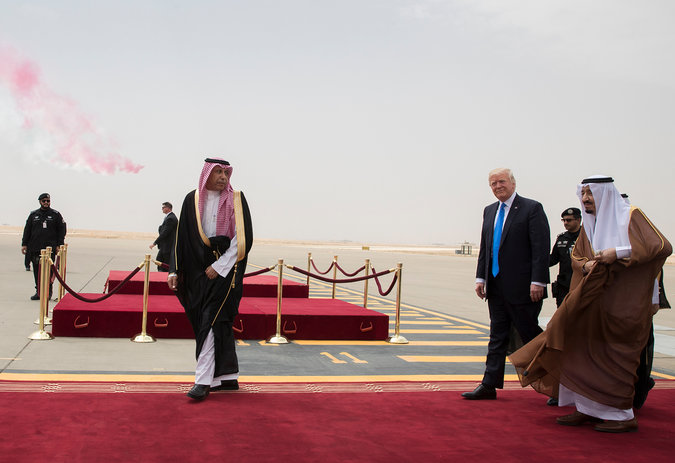
Hard to see what comes out of shocking move except social chaos / economic dislocation / complete breakdown of any remaining Sunni – Shiite amity in Arab / Muslim world. Economies of all countries involved are deeply intertwined – in hurting the other, they will insure their own pain. Given dependence of all on oil / natural gas, hard to see how one side or another doesn’t successfully block the Straits of Hormuz – meaning collapse of global oil and other energy markets. If world oil / energy markets collapse, then what ??? Experience of 70s & 8os – stagflation, combined with endemic shortages and frequent supply interruptions – doesn’t look very appealing. World economy won’t be able to stand the stresses in production / distribution / trade and investment. Just as scary, already hostile relations among Sunnis & Shiites will be polarized and militarized even further, increasing the convulsive violence already shaking Arab / Muslim world. Don’t immediately see how this one can ever be “walked back,” especially when US has already made clear it’s bought into the foolish Sunni obsession with Iran & Shiism. Top: “Don” Trump in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, in May. Trump’s blind support for Saudis encouraged other Sunni states to escalate their campaign against Qatar. Bottom: Aerial shot of stunning Doha skyline. Five Arab nations have suspended diplomatic relations with Qatar, and four of them ordered their citizens to leave the country – a logistical nightmare equal to that during the births of India and Pakistan and Israel / Palestine
For years, the tiny, energy-rich country of Qatar has carved out a niche in the Muslim world by trying to be everything to everyone.
It housed an American military base and flooded the region’s airwaves with its influential media,
all while keeping close ties to Iran and a wide selection of Islamist movements.
On Monday, five countries in the region announced that they were forcing Qatar to choose:
Its powerful neighbor Saudi Arabia, Egypt and at least three other Sunni Arab nations severed all ties with the country,
escalating their accusations that the Qatari monarchy supported Sunni Islamist terrorism and Iranian designs on the region.
Sunnis “Unleash Hell”
Those Arab nations not only abruptly suspended diplomatic relations, as they have in the past,
but also surprised many by cutting off land, air and sea travel to and from Qatar.
All but Egypt, which has 250,000 people working there, ordered their citizens to leave Qatar.
The move created an immediate crisis for Qatar,
whose only land border is with Saudi Arabia and which imports about 40% of its food from the Saudis.
Residents said that people were stocking up on food and cash.
And Qatari diplomats and citizens were scrambling to meet a 48-hour deadline to leave some Persian Gulf countries where they had been posted.
Did “Don” Trump Gave The Okay ???
Some analysts saw the sudden escalation as a sign Saudi Arabia and its allies had been emboldened by the recent visit from President Trump,
in which he publicly embraced the Saudis as a leading partner in fighting terrorism and countering Iran’s influence.
In that view, Trump, by strongly embracing the Saudis, pulled the gloves off a brawl that had long threatened to turn ugly.
But it could also end up hurting American efforts to build broader coalitions in the region,
and weaken an ally that has provided a vital base for the US military in its campaign against the Islamic State.
Randa Slim, at the Middle East Institute in Washington, said the move raised questions about
whether the Trump administration knew what it was unleashing when it further empowered the Saudis.
“Regionally, the decks are stacked against Qatar:
If denied U.S. support, the Qatari emir has no option but to back down,” Ms. Slim said.
“The question is what, if anything, will this administration do about it?”
“Don” Trump in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, in May. Trump’s strong support for the Saudis may have helped encourage other Sunni states to renew their campaign against Qatar.
The move was announced by Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Egypt, Bahrain and Yemen.
The Maldives and the eastern government in divided Libya also said they were joining in the sanctions.
But in a sign that some Saudi allies were still on the fence, neither Jordan nor Kuwait joined in.
Regional / Global Air Traffic Disrupted
Air traffic was immediately disrupted, with the United Arab Emirates suspending service to Qatar
by its three carriers, Etihad Airways, Emirates and FlyDubai, beginning Tuesday morning.
Qatar Airways was banned from Saudi airspace.
Iran: “Neighbors Are Permanent – Geography Can’t Be Changed”
The Foreign Ministry of Qatar released a statement saying the action had “no basis in fact” and was “unjustified.”
The Iranian government criticized the Saudi-led action in a diplomatically worded rebuke.
“Neighbors are permanent; geography can’t be changed,”
Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif said on his Twitter account.
“Coercion is never the solution,” Zarif said.
“Dialogue is imperative, especially during blessed Ramadan.”
Rich, Tiny Qatar Survival Strategy – Be Friends With Everybody
Qatar, one of the richest countries in the world, has used that wealth in recent years to play an outsize role in regional politics.
It has often sought to cast itself as a broker, trying to mediate the region’s intractable conflicts.
Its actions are a study in contradictions.
Qatar has good relations with Iran, but hosts the American air base.
It is helping to fight the Iranian-linked Houthi rebels in Yemen,
and it is backing insurgents fighting Tehran’s ally, President Bashar al-Assad of Syria.
Yet it has also established back channels to Iran and brokered deals with it.
Tensions had been building for years.
There was Qatar’s support for the Muslim Brotherhood,
which challenged the established order in Egypt before being suppressed by the current government.
Qatar also has supported Hamas, which governs the Gaza Strip and is a rival of the Palestinian Authority.
And the broadcasts of the Pan-Arab news network Al Jazeera, which Qatar funds, have long ruffled feathers across the Middle East.
Qatar’s rivals have also faulted it for condoning fund-raising for militant Islamist groups fighting in Syria —
including groups tied to Al Qaeda and the Islamic State —
although several of the other Sunni-led monarchies in the region have played similar roles.
Qatar’s Main “Sin” Support Of NOT Sunni Islamists — But Iran
Qatar’s opponents have added a third allegation to those grievances:
that it is conspiring with their regional rival, Iran.
That is in part because Qatar has taken an important back-channel role with Iran to defuse points of contention in the Syrian war.
It has repeatedly brokered hostage and prisoner exchanges,
paying millions of dollars to insurgent and militant groups in the deals.
The most notable of those deals came in April,
when Qatar paid a huge ransom to free 26 members of a Qatari falcon-hunting party, including members of the royal family,
who had been taken hostage by Iran-backed militiamen in Iraq.
Officials said Qatar paid millions of dollars, most of which was said to have gone to militia leaders loyal to Iran.
Qatar is also a sponsor of the Four Towns agreement in Syria, negotiated with Iran and Hezbollah,
in which civilians trapped under siege by government troops or by rebel forces have been bused to other areas.
The deals are hailed by some as the only way to rescue civilians, but they have been criticized by others as forced displacements.
Arrival Of Cyber-Hacking In Middle East Has Immediate Explosive Effect
The Qataris complain that they are being targeted.
They say they were the victims of a cyberattack last month when the state news media outlet released a false report,
quoting the emir, Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad al-Thani, as referring to tension with Washington over Iran policy,
and saying that Trump might not be in power for long.
The F.B.I. was investigating and has not yet released its findings.
But one analyst, Gerd Nonneman, a professor of international relations and gulf studies at Georgetown University’s campus in Doha, Qatar, said
F.B.I. and British intelligence officials had “no doubt” the article on the emir was the result of a hack.
“This is the first time we’ve seen this level of cyberattack in the gulf, the hacking of a news site,” Nonneman said.
“We’ve not seen these countries engage in these types of online attacks before, at least against each other.
It is new ground for them.”
The isolation of Qatar was widely being taken as a clear message from Saudi Arabia that in the new order, no softness on Iran would be tolerated.
But even though Saudi anger at the Qataris has brewed for a long time, on several fronts, several analysts believe Trump’s visit provided a moment to act.
“It is entirely possible that the catalyst to this crisis was the feeling in Riyadh and Abu Dhabi
that the U.S. under the Trump administration is aligned with them,”
said Emile Hokayem, a Middle East analyst with the International Institute for Strategic Studies.
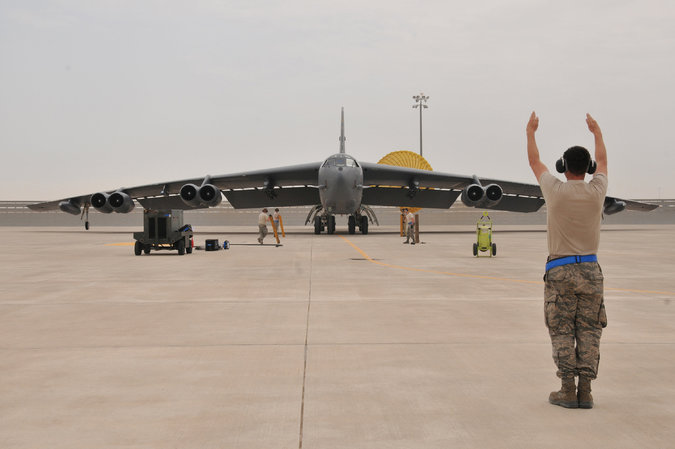
The Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar last year, home of the American-led air war against the Islamic State. Credit Tech. Sgt. Terrica Y. Jones/U.S. Air Force, via Reuters
Yezid Sayigh, a senior fellow at the Carnegie Middle East Center in Beirut, said
the new moves reflected a “bullishness” prompted by the Trump administration’s stances —
on the confrontation with Iran and on a willingness to look the other way on human rights violations.
Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates are getting “no U.S. pushback” on human rights or on the Yemen intervention, he said,
while “Egypt also feels off the hook with Trump, and is using the opportunity to
- repair ties with the Saudis,
- reinforce with the Emiratis and
- be more assertive in Libya.”
But the move carries perils for the other countries as well, Sayigh warned.
“Cutting relations with Qatar suggests a worrying readiness to be assertive and belligerent,” he said,
adding that it “may prove to be a case of overreach.”
But the escalating confrontation between Qatar and other Sunni-led Arab states presents a new and unwelcome complication for the US military,
which has made strenuous efforts to forge a broad coalition against the Islamic State.
Secretary of State Rex W. Tillerson and Defense Secretary Jim Mattis —
who appeared in their first joint news conference, in Sydney, Australia, after talks with their Australian counterparts on Monday —
insisted that it would not undermine the fight against the Islamic State, also known as ISIS or ISIL.
“I am confident there will be no implications,” Mattis said.
But there were few immediate answers to some difficult questions for American operations.
Insane Move Only Creates Chaos In Region / World
How, for example, can the American-led air campaign include warplanes from Bahrain, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates
if those governments will no longer allow their military representatives to be based at, or even to visit, a major US command center?
Beyond the military difficulties, several multinational corporations have operations in the feuding nations.
A Saudi call for companies to withdraw from Qatar could present international executives with difficult choices about where to do business.
Qatar is hosting the 2022 World Cup, for instance,
and is building facilities for the tournament that are part of an ambitious construction boom,
including creating branches of major international museums and universities.
About 80% of Qatar’s residents are foreign workers,
including white-collar professionals and construction and service workers.
There are about 250,000 Egyptians working in Qatar,
which is perhaps why Cairo did not call for its citizens to leave as Saudi Arabia did.
Source: 5 Arab Nations Move to Isolate Qatar, Putting the U.S. in a Bind – The New York Times


